First of all, let us understand what is Paradigm? Paradigm, in simpler terms, can be referred to as a pattern or model or a blueprint. It is a distinct set of concepts or patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitutes legitimate contributions to a field.
So Programming Paradigm can be inferred as a model for programming. How programs and in general programming languages should be written, what patterns they should follow, and how these languages work. A programming paradigm is a style, or “way,” of programming.
There are so many such paradigms out there, but I will be talking about some of the most widely used and followed paradigms. I hope you understand the meaning of "Programming Paradigm".
Programming languages are based on a certain paradigm, a set of rules which needs to be followed while working with that language.
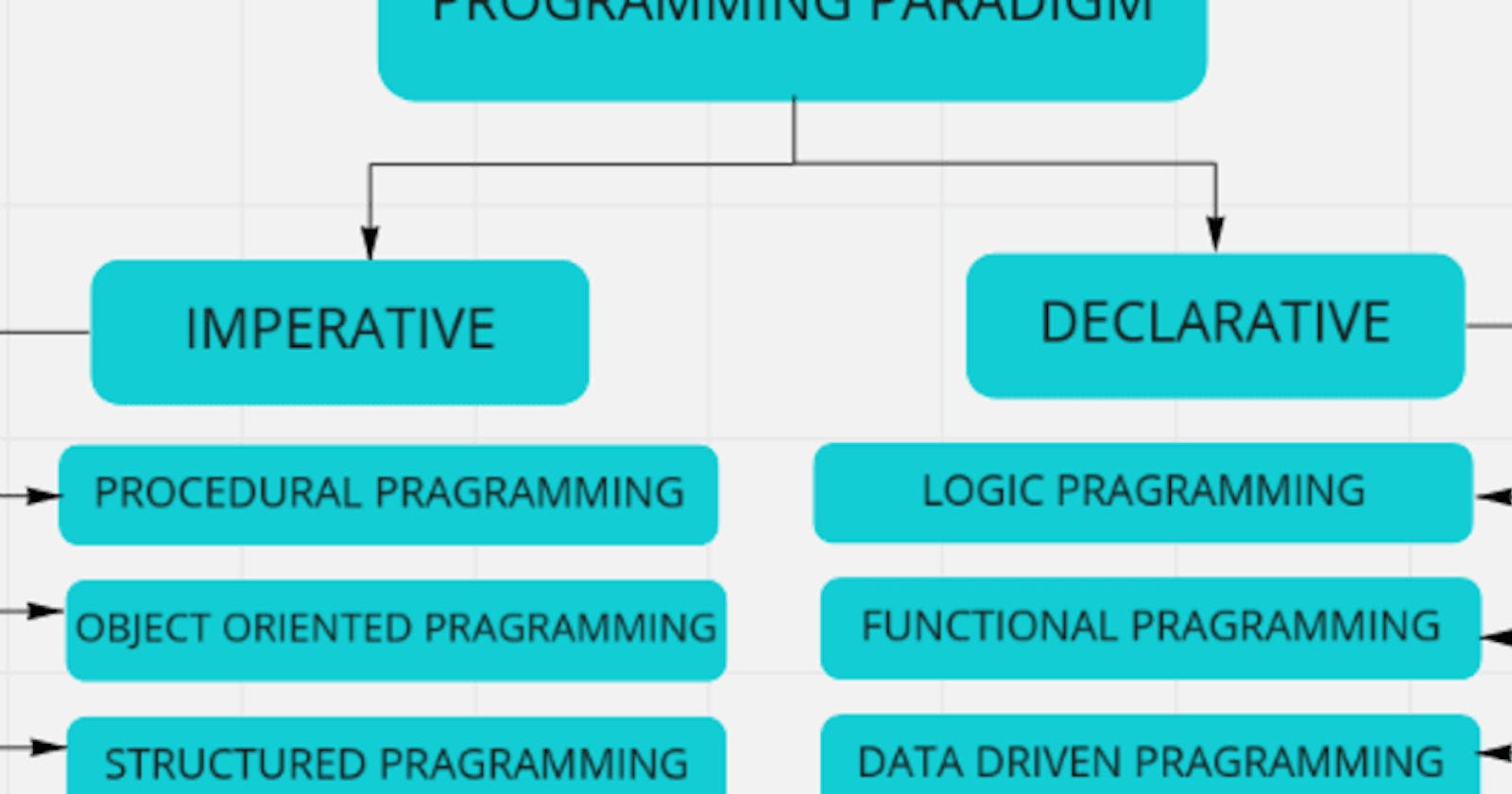
Programming Paradigms can be generally divided into 2 main kinds, Imperative, and Declarative Programming Paradigm. These 2 can be further divided into different kinds of paradigms in use today.
1. IMPERATIVE PROGRAMMING
It is one of the oldest programming paradigms and is based on Von Neumann's architecture. Its name comes from the Latin imperare meaning “command” or instructions. It works as closely as possible with the system and thus has a close relation to machine architecture.
It works by changing the program state through assignment statements. It performs step by step tasks by changing state. Older languages like Pascal and C, as well as all assembly languages are based on it.
1a. PROCEDURAL PROGRAMMING
The procedural programming paradigm extends the imperative approach with the possibility of dividing algorithms into more manageable sections. This paradigm emphasizes procedure in terms of the underlying machine model. There is no difference between the procedural and imperative approaches.
It has the ability to reuse the code and it was a boon at that time when it was in use because of its reusability. Depending on the programming language, these are referred to as sub-programs, routines, or functions.
The purpose of this division is to make the programming code clearer and to prevent unnecessary code repetitions. C is an example of procedural programming language.
1b. OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
Object Oriented Programming paradigm is one of the most popular and widely used paradigms. Most of today's high-level languages support object oriented programming or are object oriented programming (OOP) languages. Examples are Java, C++, Python, etc.
It is based on classes and objects which are meant for communication. The smallest and basic entity is an object and all kinds of computation are performed on the objects only. More emphasis is on data rather procedure.
It can handle almost all kinds of real life problems which are today in the scenario.
1c. STRUCTURED PROGRAMMING
The structured programming method is a simplified form of imperative programming. The crucial difference from the basic principle is that instead of absolute jump commands (instructions that lead to processing continuing at another point instead of the next command), this software programming paradigm makes use of control loops and structures.
An example is the use of “do...while”, which executes an instruction automatically for as long as a particular condition is true (at least once).
2. DECLARATIVE PROGRAMMING
Declarative Programming is divided as Logic, Functional, Data. In computer science, the term declarative programming is a style of building programs that express the logic of a computation without talking about its control flow.
The fundamental principle of declarative programming is that it describes the desired result. The focus is on what needs to be done rather than how it should be done emphasizing what the code is doing.
This is the only difference between imperative (how to do) and declarative (what to do) programming paradigms.
2a. LOGIC PROGRAMMING
Logic programming, also known as predicate programming, is based on mathematical logic. Instead of a sequence of instructions, it contains a set of principles, which can be understood as a collection of facts and assumptions.
It can be termed as an abstract model of computation. It would solve logical problems like puzzles, series, etc.
In logic programming we have a knowledge base that we know before and along with the question and knowledge base which is given to the machine, it produces results. Prolog is a logic programming language.
2b. FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
Functions exist in every higher-level programming language. However, the functional approach in software development deals with functions in a very particular way.
The functional programming paradigms have their roots in mathematics and it is language independent. The key principle of this paradigm is the execution of a series of mathematical functions.
A functionally programmed program is made up of a string of function calls, where each program section can be understood as a function. In functional programming, the functions can take on different forms.
For example, they can be linked to one another like data or be used in the form of parameters. In addition, they can subsequently be used as function results.
2c. DATA DRIVEN PROGRAMMING
As the name suggests, this paradigm is driven by data i.e. it revolves around data. Data is the main component of this paradigm. Program statements are defined by data rather than hard-coding a series of steps.
Several programming languages are developed mostly for database applications such as SQL.
This was the second article of the series #intro-to-programming. Please share your thoughts about the article.
If you liked the article, then please give it a 👍
You can check out my blog codeunlock.in to find my other articles.